Extreme heat events are becoming the norm. This past summer in the U.S. alone, several states experienced week-long stretches of abnormally high temperatures. In fact, July 2023 was the hottest month ever recorded on Earth. These events stretch power grids to their limits, requiring an all-hands-on-deck approach from power generation resources to keep the lights on. With their inherent flexibility, energy storage assets can play a critical role in renewable energy shifting to peak demand times and supporting grid stability.
During times of extreme weather, accurate price forecasting and bid optimization are even more crucial to owners and operators of storage assets that are looking to help keep the grid stable, serve load, and maximize revenue at the same time.
As electricity generation from renewable energy sources continues to increase and replace carbon-emitting thermal generation on the California Independent System Operator (CAISO) grid, it is making the grid cleaner but also creates challenges in integrating this power. First, it’s hard to fully make use of this energy due to California’s infamous “duck curve” - a glut of renewable generation when the sun is high and lower generation when the sun is down, but demand is high.
In addition, the second-by-second uncertainty and fluctuation in renewables generation from environmental conditions make it challenging to anticipate when renewable energy will be available. During periods of extreme heat across the CAISO region, these problems are further exacerbated by substantial increases in load.
Energy storage, as a flexible, bi-directional asset class, is a crucial part of solving these problems. However, fully leveraging it at scale requires advanced electricity price forecasting and advanced bid optimization to know when and how to use storage at scale on the grid. Owners and operators of utility-scale storage assets are increasingly turning to automated bid optimization tools integrated with price forecasting to help balance the grid and realize the revenue benefits of doing so.
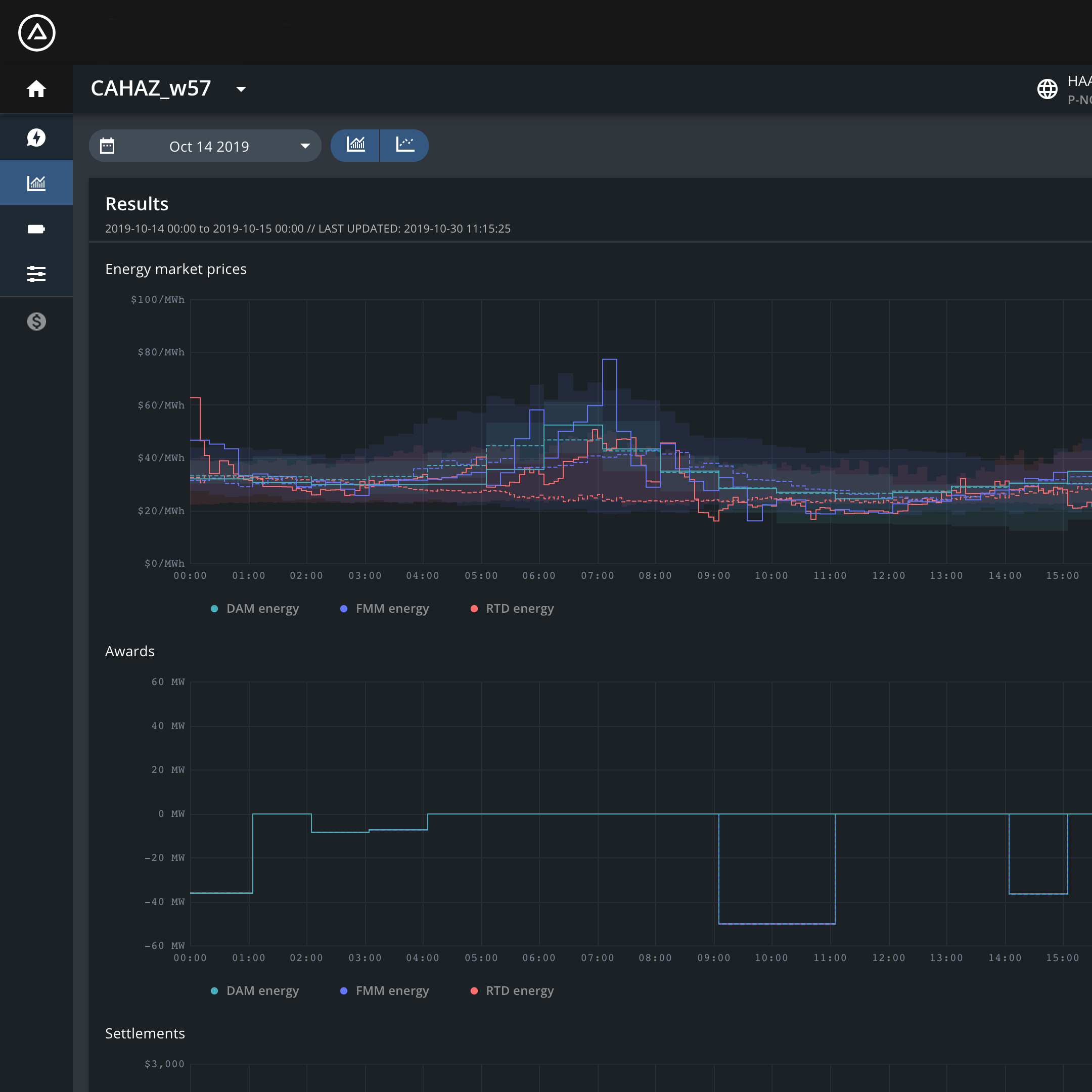
In one period of extreme heat this summer on August 16, Fluence Mosaic™, our bid optimization software, helped CAISO meet load and frequency control and helped customers earn over $3,700/MW throughout the day by anticipating the volatility and adjusting bid schedules appropriately.
Let’s examine this extreme weather event, when above-average temperatures brought extremely tight conditions to CAISO, especially in certain times of the day, such as hour ending 20 (HE20) when Day-Ahead Resource Adequacy (DA RA) capacity was mere MWs above the forecasted net demand.
Chart 1: CAISO RA Capacity vs. Net Demand and Reserves for Aug. 16, 2023

These tight conditions in this hour were largely due to the timing of when solar production declines versus when overall demand begins to decline.
Chart 2: CAISO Solar Generation for Aug. 16, 2023

In chart 2, we can see that the solar generation ramps up starting at 6:00, reaching a peak at noon, and ramps down until 19:30. However, the demand peaks between 18:00 and 21:00 as shown in chart 1. And so, by 19:30, there is no solar generation to serve the rise in demand. This is where energy storage really shines in these conditions and helps make up the difference by time-shifting energy that was produced earlier in the day to the tight times later in the day.
Chart 3: CAISO Supply for Aug. 16, 2023

Energy storage operators face challenging decisions when operating in market conditions like these where demand peaks when renewable generation is not available. Pre-set strategies for product participation can often miss critical moments like this and fail to help the grid meet demand. Quality forecasting and optimization can produce strategies that automatically change to meet the needs of the grid as market conditions change, both helping the grid maintain stability and the storage operator capture revenue.
Mosaic for CAISO works hard to solve these problems for energy storage operators. Mosaic’s node-specific price forecast models use machine learning and a carefully curated blend of exogenous variables to predict market prices with uncertain information across a 72-hour horizon. These forecasts are fed into multi-day stochastic optimizations tuned to maximize revenue across the full optimization horizon while staying within the contractual, operational, and strategic constraints as defined by the storage operator. This approach to energy storage bidding leads to market participation that can successfully capture changing market opportunities and help provide maximal value to the grid.
Mosaic Day-Ahead Price Forecast for Aug. 16, 2023

Turning back to the heatwave on August 16, Mosaic’s price forecast models predicted high prices for energy (orange line), regulation up (green line), and spin (blue line) products in the evening hours, with a peak in HE20 (Hour Ending 20: 19:00 – 20:00 PST).
In this situation, it may seem intuitive to discharge the resource in HE20 to capture the high energy price. However, this isn’t necessarily capturing the most revenue, nor is it leveraging the capabilities of the resource to assist the grid. As chart 5 shows, Mosaic’s optimization identified that the best pathway was to offer regulation up in the two highest-priced energy hours of the day. The orange line shows the energy schedule, green bars show the range of possible regulation up dispatch, blue bars show the range of possible spin dispatch, and the purple bars show the range of possible regulation down dispatch.
Mosaic Day-Ahead Awards for Aug. 16, 2023

The optimization considers the hourly expected throughput from regulation, with HE19 set at 12.12% of awarded capacity and HE20 set at 15% of awarded capacity for this resource on this day. That means this decision is optimal for two main reasons:
- The regulation up price is very close to the energy price, so the revenue generated from the energy throughput that will come from the regulation up dispatch will make up the difference between the regulation up price and energy price.
- The reduced throughput of regulation up as compared to an energy discharge of the same award quantity means the energy storage retains more energy to sell in later hours (HE21 & HE23), still at very attractive prices.
On balance, this schedule generated more revenue than a strategy that just assumes it is best to discharge in the top-priced energy hours of the day. It also extended the services the storage can provide to the grid, meeting more needs across more intervals.
There is prohibitive complexity in making these decisions manually across energy and ancillary services products while also considering market rules like Resource Adequacy (RA), CAISO’s own model of state of charge (SOC), an asset’s contractual obligations, warranty limitations, an organization’s risk tolerances, and maintaining a feasible solution based on a more realistic model of SOC. All this complexity necessitates algorithmic-based decision making to truly find the optimal schedule for a day.

Heatwaves have become the new normal, with extreme temperatures becoming increasingly frequent. These occurrences put power grids under tremendous strain, demanding a collaborative effort from power generation resources to ensure uninterrupted electricity supply. With their inherent flexibility, energy storage assets can play a critical role in renewable energy shifting to peak demand times and supporting grid stability. As an experienced technology provider with a strong presence in CAISO, Fluence helps customers simplify these complex bidding decisions.
Want to unlock the full revenue potential of your energy storage with bid optimization solutions?